Authored by Tony Feng
Created on Nov 18th, 2022
Last Modified on Nov 18th, 2022
Intro
This sereis of posts contains a summary of materials and readings from the course CSCI 1460 Computational Linguistics that I’ve taken @ Brown University. The class aims to explore techniques regarding recent advances in NLP with deep learning. I posted these “Notes” (what I’ve learnt) for study and review only.
Formal Grammars
Terminologies
- Language: set of strings
- Grammar: set of rewrite rules which define a language
- $N$: a set of non-terminal symbols (variables)
- ${\Sigma}$: a set of terminal symbols (disjoint from $N$)
- $R$: a set of production rules each of the form $A$ -> $B$
- $S$: a designated start symbol (member of $N$)
Formal Grammar and Automata
- Grammars and Automata are two ways of modeling the same thing
- Grammars are used to generate languages
- Automata are used to recognize languages
- Regular language
- $A$ -> $Ba$ (i.e., one NT symbol, always at the beginning or end)
- It doesn’t work when language requires recursion
- It can be recognized by an finite-state automaton
- Context-Free Languages:
- $A$ -> $a$ (where $a$ can be any mix of terminals and non-terminals)
- Language can be recognized by a pushdown automaton (an automaton that uses a stack to maintain memory)
- “context free” because rule can be applied to the nonterminal regardless of its context
Constituency Parsing
Constituency Grammar
- “Phrase Structure Grammar”
- Sentences -> Phrases

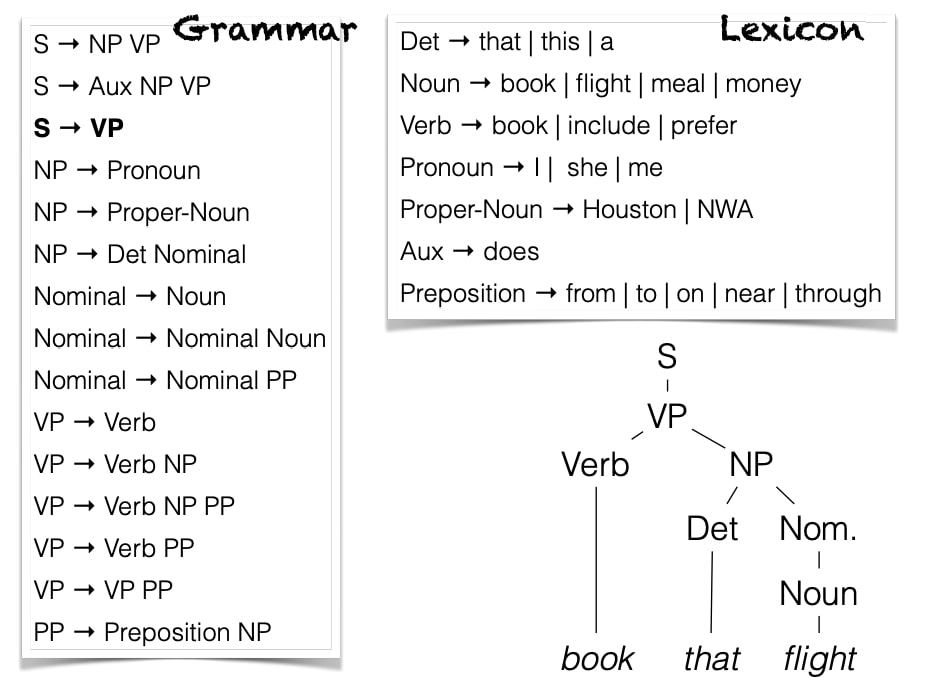

CKY Parsing
- Dynamic Programming
- Basic idea: find a parse for words $i$ through $j$ by combining parses for words $i$ through $k$ with parses for works $k$ through $j$.

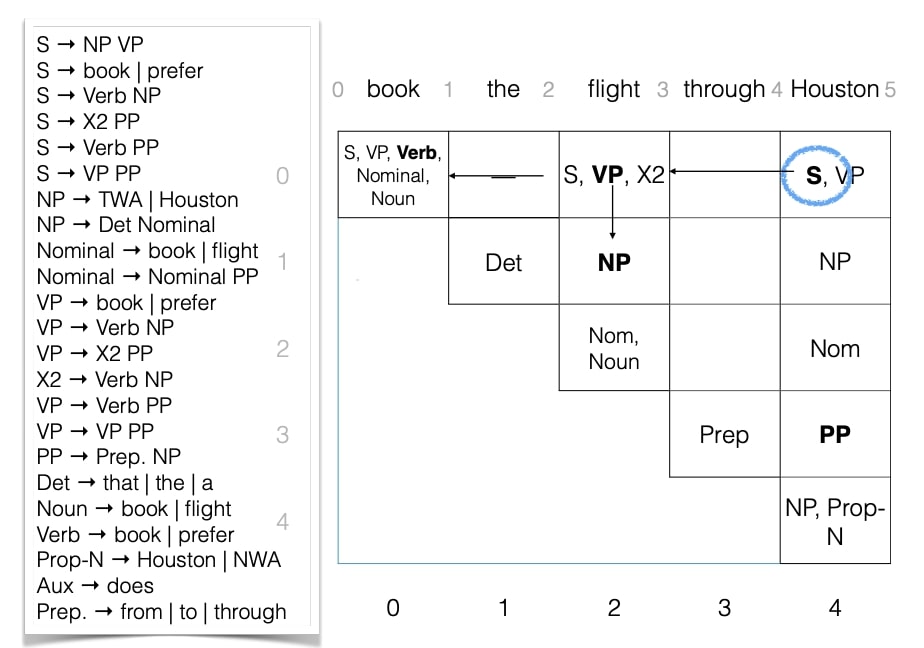

Dependency Parsing
Dependency Grammar
- The goal is to make explicit relationships between words
- Typically, a verb is at the ROOT
- The core of the sentence is subject-verb-object
- Additional clauses/modifiers hang off of these
Shift-Reduce Algorithm
- Dependency parses are represented as a directed graph with Vertices (V) and Arcs (A)
- V is roughly the set of words and punctuation
- It is constrained to be single-rooted trees
- Shift-Reduce Algorithm
- Transition-Based Parser
- Basic idea
- Progress left to right in the sentence, maintain a stack
- At each step, either:
- assign this word to be the head of previous word,
- assign a previously seen word to be the head of this word,
- defer decision to a later step
- Design about 1, 2, or 3 is made by a supervised classifier
- Three Operations
- LeftArc: set stack[0] as head of stack[1]; remove stack[1] from stack
- RightArc: set stack[1] as head of stack[0]; remove stack[0] from stack
- Shift: Push new word onto stack
- Precondition: ROOT can’t have a parent

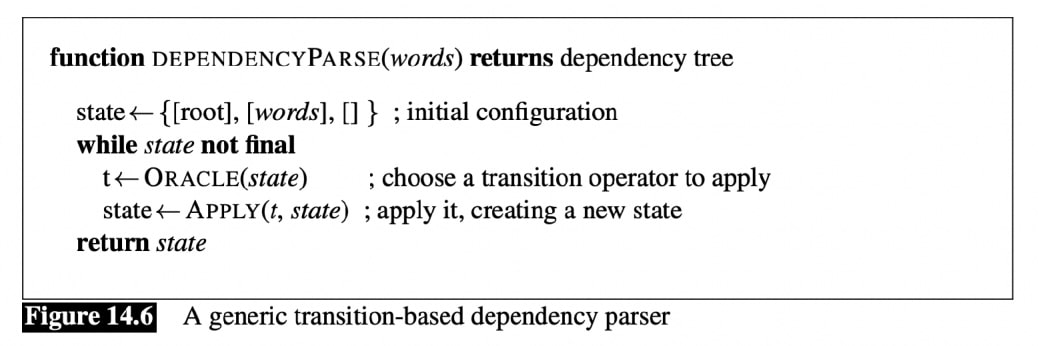

- Training the Oracle